Input interpretation
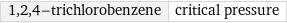
1, 2, 4-trichlorobenzene | critical pressure
Result
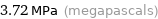
3.72 MPa (megapascals)
Unit conversions
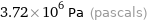
3.72×10^6 Pa (pascals)

3.72×10^6 N/m^2 (newtons per square meter)
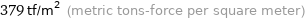
379 tf/m^2 (metric tons-force per square meter)
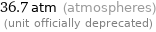
36.7 atm (atmospheres) (unit officially deprecated)
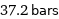
37.2 bars
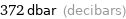
372 dbar (decibars)
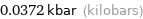
0.0372 kbar (kilobars)
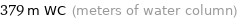
379 m WC (meters of water column)

0.379 km WC (kilometers of water column)
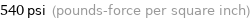
540 psi (pounds-force per square inch)
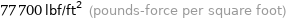
77700 lbf/ft^2 (pounds-force per square foot)
Comparisons as pressure

≈ 0.37 × pressure exerted by a 45 kg woman wearing stiletto heels ( ≈ 1×10^7 Pa )
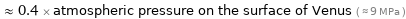
≈ 0.4 × atmospheric pressure on the surface of Venus ( ≈ 9 MPa )
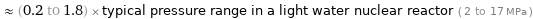
≈ (0.2 to 1.8) × typical pressure range in a light water nuclear reactor ( 2 to 17 MPa )
Corresponding quantity
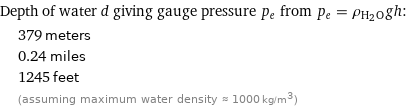
Depth of water d giving gauge pressure p_e from p_e = ρ_(H_2O)gh: | 379 meters | 0.24 miles | 1245 feet | (assuming maximum water density ≈ 1000 kg/m^3)