Input interpretation
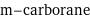
m-carborane
Chemical names and formulas
![formula | C_2H_12B_10 Hill formula | B_10C_2H_12 name | m-carborane alternate names | 1, 7-dicarbadodecaborane(12) | 2\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 3\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 4\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 5\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 6\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 7\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 8\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 9\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 11\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 12\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\)-decaborabicyclo[8.1.1]dodecane mass fractions | B (boron) 80.6% | C (carbon) 17.9% | H (hydrogen) 1.5%](../image_source/101a64957dcffdf5203a6f8024ec6433.png)
formula | C_2H_12B_10 Hill formula | B_10C_2H_12 name | m-carborane alternate names | 1, 7-dicarbadodecaborane(12) | 2\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 3\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 4\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 5\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 6\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 7\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 8\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 9\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 11\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\), 12\!\(\*SuperscriptBox[\(λ\), \(2\)]\)-decaborabicyclo[8.1.1]dodecane mass fractions | B (boron) 80.6% | C (carbon) 17.9% | H (hydrogen) 1.5%
Lewis structure
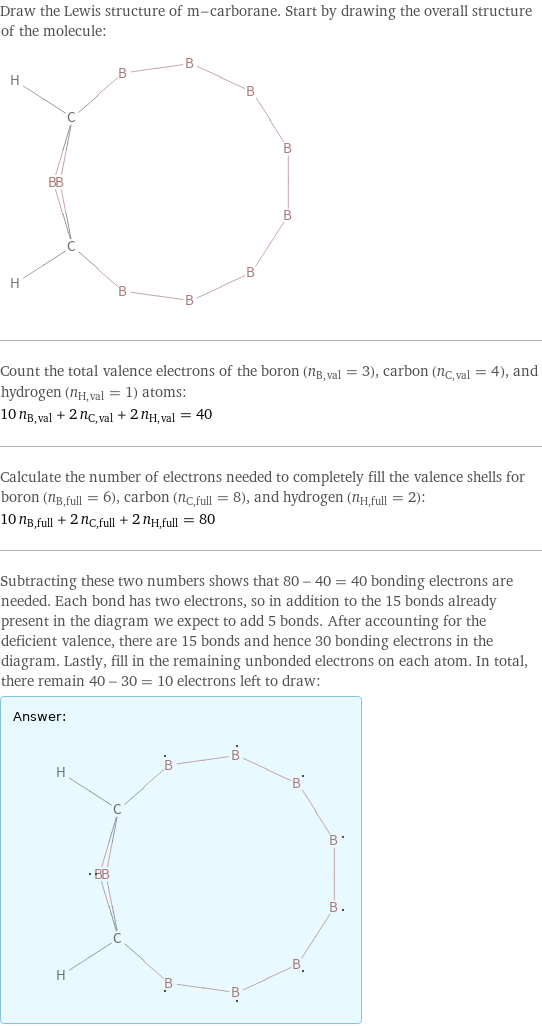
Draw the Lewis structure of m-carborane. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the boron (n_B, val = 3), carbon (n_C, val = 4), and hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) atoms: 10 n_B, val + 2 n_C, val + 2 n_H, val = 40 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for boron (n_B, full = 6), carbon (n_C, full = 8), and hydrogen (n_H, full = 2): 10 n_B, full + 2 n_C, full + 2 n_H, full = 80 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 80 - 40 = 40 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 15 bonds already present in the diagram we expect to add 5 bonds. After accounting for the deficient valence, there are 15 bonds and hence 30 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 40 - 30 = 10 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
Basic properties

molar mass | 134.1 g/mol
Units

Chemical identifiers
CAS number | 16986-24-6 RTECS number | HS9290000 MDL number | MFCD00151574