Input interpretation
hafnium (chemical element) | manganese (chemical element) | ruthenium (chemical element)
Periodic table location
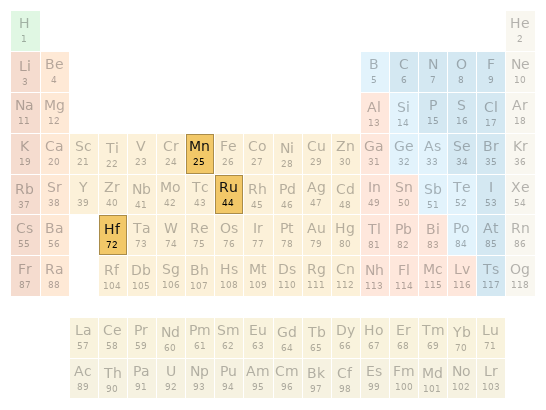
Periodic table location
Images

Images
Basic elemental properties
![| hafnium | manganese | ruthenium atomic symbol | Hf | Mn | Ru atomic number | 72 | 25 | 44 short electronic configuration | [Xe]6s^24f^145d^2 | [Ar]4s^23d^5 | [Kr]5s^14d^7 Aufbau diagram | 5d 4f 6s | 3d 4s | 4d 5s block | d | d | d group | 4 | 7 | 8 period | 6 | 4 | 5 atomic mass | 178.49 u | 54.938044 u | 101.07 u half-life | (stable) | (stable) | (stable)](../image_source/d14efde06c8e1c727111105c5a87eb69.png)
| hafnium | manganese | ruthenium atomic symbol | Hf | Mn | Ru atomic number | 72 | 25 | 44 short electronic configuration | [Xe]6s^24f^145d^2 | [Ar]4s^23d^5 | [Kr]5s^14d^7 Aufbau diagram | 5d 4f 6s | 3d 4s | 4d 5s block | d | d | d group | 4 | 7 | 8 period | 6 | 4 | 5 atomic mass | 178.49 u | 54.938044 u | 101.07 u half-life | (stable) | (stable) | (stable)
Thermodynamic properties
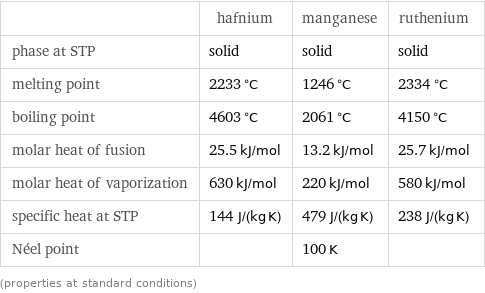
| hafnium | manganese | ruthenium phase at STP | solid | solid | solid melting point | 2233 °C | 1246 °C | 2334 °C boiling point | 4603 °C | 2061 °C | 4150 °C molar heat of fusion | 25.5 kJ/mol | 13.2 kJ/mol | 25.7 kJ/mol molar heat of vaporization | 630 kJ/mol | 220 kJ/mol | 580 kJ/mol specific heat at STP | 144 J/(kg K) | 479 J/(kg K) | 238 J/(kg K) Néel point | | 100 K | (properties at standard conditions)
Material properties
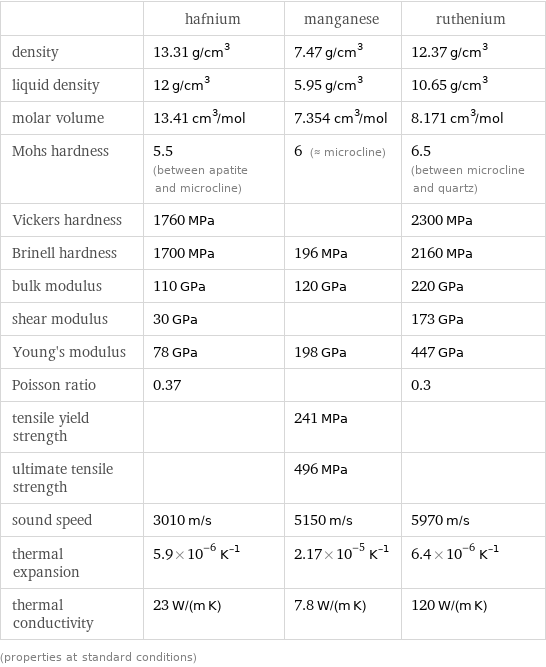
| hafnium | manganese | ruthenium density | 13.31 g/cm^3 | 7.47 g/cm^3 | 12.37 g/cm^3 liquid density | 12 g/cm^3 | 5.95 g/cm^3 | 10.65 g/cm^3 molar volume | 13.41 cm^3/mol | 7.354 cm^3/mol | 8.171 cm^3/mol Mohs hardness | 5.5 (between apatite and microcline) | 6 (≈ microcline) | 6.5 (between microcline and quartz) Vickers hardness | 1760 MPa | | 2300 MPa Brinell hardness | 1700 MPa | 196 MPa | 2160 MPa bulk modulus | 110 GPa | 120 GPa | 220 GPa shear modulus | 30 GPa | | 173 GPa Young's modulus | 78 GPa | 198 GPa | 447 GPa Poisson ratio | 0.37 | | 0.3 tensile yield strength | | 241 MPa | ultimate tensile strength | | 496 MPa | sound speed | 3010 m/s | 5150 m/s | 5970 m/s thermal expansion | 5.9×10^-6 K^(-1) | 2.17×10^-5 K^(-1) | 6.4×10^-6 K^(-1) thermal conductivity | 23 W/(m K) | 7.8 W/(m K) | 120 W/(m K) (properties at standard conditions)
Electromagnetic properties
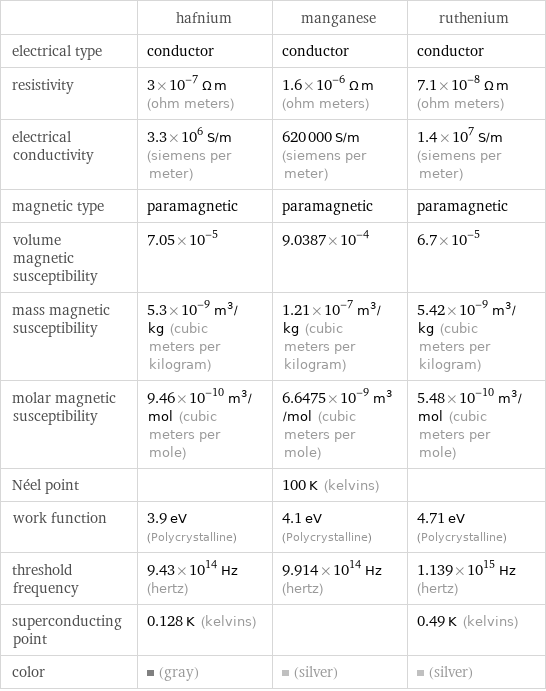
| hafnium | manganese | ruthenium electrical type | conductor | conductor | conductor resistivity | 3×10^-7 Ω m (ohm meters) | 1.6×10^-6 Ω m (ohm meters) | 7.1×10^-8 Ω m (ohm meters) electrical conductivity | 3.3×10^6 S/m (siemens per meter) | 620000 S/m (siemens per meter) | 1.4×10^7 S/m (siemens per meter) magnetic type | paramagnetic | paramagnetic | paramagnetic volume magnetic susceptibility | 7.05×10^-5 | 9.0387×10^-4 | 6.7×10^-5 mass magnetic susceptibility | 5.3×10^-9 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) | 1.21×10^-7 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) | 5.42×10^-9 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) molar magnetic susceptibility | 9.46×10^-10 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) | 6.6475×10^-9 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) | 5.48×10^-10 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) Néel point | | 100 K (kelvins) | work function | 3.9 eV (Polycrystalline) | 4.1 eV (Polycrystalline) | 4.71 eV (Polycrystalline) threshold frequency | 9.43×10^14 Hz (hertz) | 9.914×10^14 Hz (hertz) | 1.139×10^15 Hz (hertz) superconducting point | 0.128 K (kelvins) | | 0.49 K (kelvins) color | (gray) | (silver) | (silver)
Reactivity
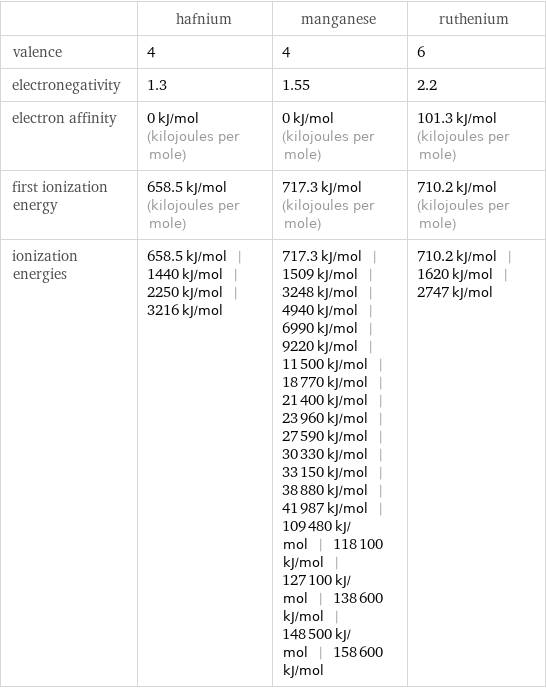
| hafnium | manganese | ruthenium valence | 4 | 4 | 6 electronegativity | 1.3 | 1.55 | 2.2 electron affinity | 0 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 0 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 101.3 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) first ionization energy | 658.5 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 717.3 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 710.2 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) ionization energies | 658.5 kJ/mol | 1440 kJ/mol | 2250 kJ/mol | 3216 kJ/mol | 717.3 kJ/mol | 1509 kJ/mol | 3248 kJ/mol | 4940 kJ/mol | 6990 kJ/mol | 9220 kJ/mol | 11500 kJ/mol | 18770 kJ/mol | 21400 kJ/mol | 23960 kJ/mol | 27590 kJ/mol | 30330 kJ/mol | 33150 kJ/mol | 38880 kJ/mol | 41987 kJ/mol | 109480 kJ/mol | 118100 kJ/mol | 127100 kJ/mol | 138600 kJ/mol | 148500 kJ/mol | 158600 kJ/mol | 710.2 kJ/mol | 1620 kJ/mol | 2747 kJ/mol
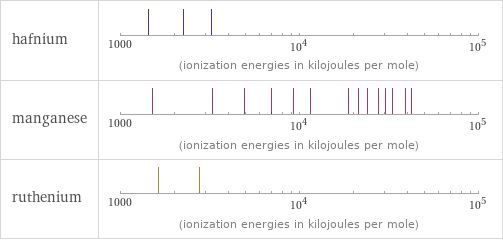
Reactivity
Atomic properties
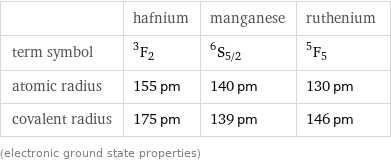
| hafnium | manganese | ruthenium term symbol | ^3F_2 | ^6S_(5/2) | ^5F_5 atomic radius | 155 pm | 140 pm | 130 pm covalent radius | 175 pm | 139 pm | 146 pm (electronic ground state properties)
Abundances
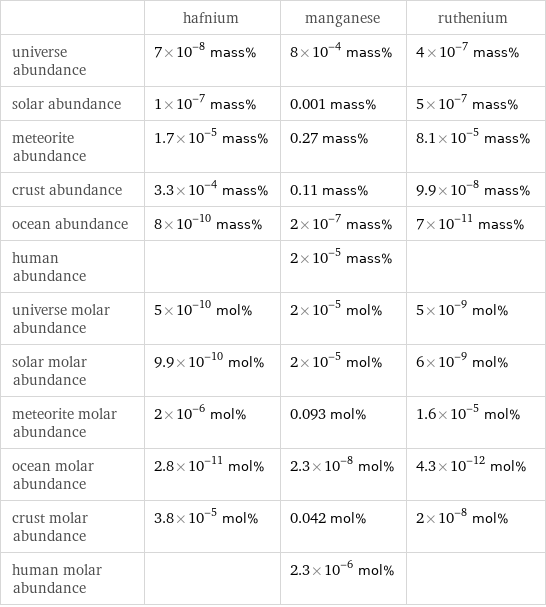
| hafnium | manganese | ruthenium universe abundance | 7×10^-8 mass% | 8×10^-4 mass% | 4×10^-7 mass% solar abundance | 1×10^-7 mass% | 0.001 mass% | 5×10^-7 mass% meteorite abundance | 1.7×10^-5 mass% | 0.27 mass% | 8.1×10^-5 mass% crust abundance | 3.3×10^-4 mass% | 0.11 mass% | 9.9×10^-8 mass% ocean abundance | 8×10^-10 mass% | 2×10^-7 mass% | 7×10^-11 mass% human abundance | | 2×10^-5 mass% | universe molar abundance | 5×10^-10 mol% | 2×10^-5 mol% | 5×10^-9 mol% solar molar abundance | 9.9×10^-10 mol% | 2×10^-5 mol% | 6×10^-9 mol% meteorite molar abundance | 2×10^-6 mol% | 0.093 mol% | 1.6×10^-5 mol% ocean molar abundance | 2.8×10^-11 mol% | 2.3×10^-8 mol% | 4.3×10^-12 mol% crust molar abundance | 3.8×10^-5 mol% | 0.042 mol% | 2×10^-8 mol% human molar abundance | | 2.3×10^-6 mol% |