Input interpretation

alkaline earth metals | specific heat at STP
Summary
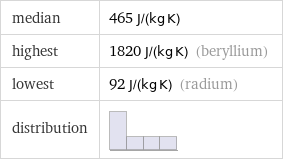
median | 465 J/(kg K) highest | 1820 J/(kg K) (beryllium) lowest | 92 J/(kg K) (radium) distribution |
Units

Ranked values
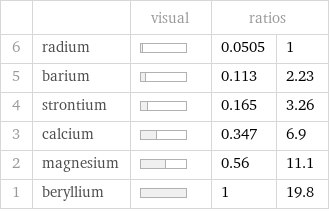
| | visual | ratios | 6 | radium | | 0.0505 | 1 5 | barium | | 0.113 | 2.23 4 | strontium | | 0.165 | 3.26 3 | calcium | | 0.347 | 6.9 2 | magnesium | | 0.56 | 11.1 1 | beryllium | | 1 | 19.8
Specific heat at STP rankings
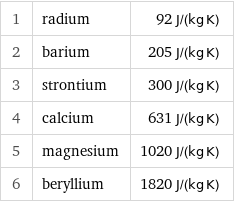
1 | radium | 92 J/(kg K) 2 | barium | 205 J/(kg K) 3 | strontium | 300 J/(kg K) 4 | calcium | 631 J/(kg K) 5 | magnesium | 1020 J/(kg K) 6 | beryllium | 1820 J/(kg K)
Unit conversions for median specific heat at STP 465 J/(kg K)
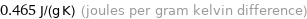
0.465 J/(g K) (joules per gram kelvin difference)
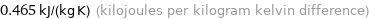
0.465 kJ/(kg K) (kilojoules per kilogram kelvin difference)
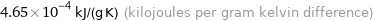
4.65×10^-4 kJ/(g K) (kilojoules per gram kelvin difference)

465 J/(kg °C) (joules per kilogram degree Celsius difference)
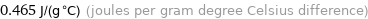
0.465 J/(g °C) (joules per gram degree Celsius difference)

0.111 BTU_IT/(lb °F) (IT British thermal units per pound degree Fahrenheit difference)
Comparisons for median specific heat at STP 465 J/(kg K)
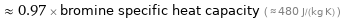
≈ 0.97 × bromine specific heat capacity ( ≈ 480 J/(kg K) )
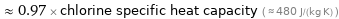
≈ 0.97 × chlorine specific heat capacity ( ≈ 480 J/(kg K) )
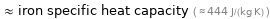
≈ iron specific heat capacity ( ≈ 444 J/(kg K) )
Thermodynamic properties
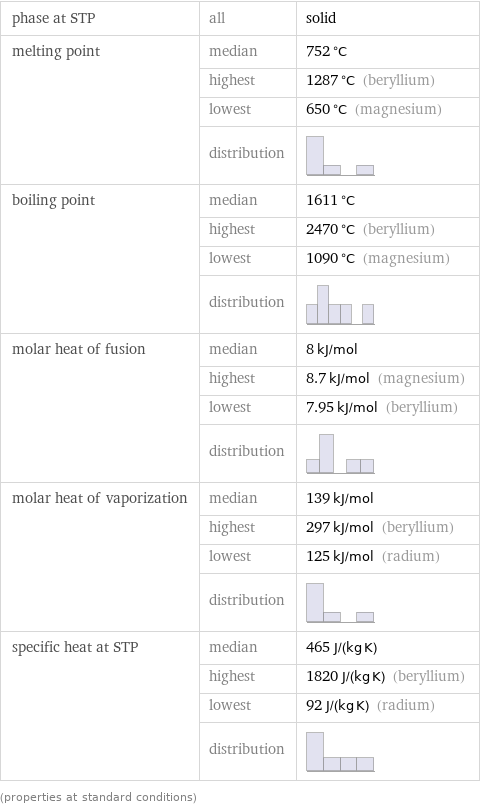
phase at STP | all | solid melting point | median | 752 °C | highest | 1287 °C (beryllium) | lowest | 650 °C (magnesium) | distribution | boiling point | median | 1611 °C | highest | 2470 °C (beryllium) | lowest | 1090 °C (magnesium) | distribution | molar heat of fusion | median | 8 kJ/mol | highest | 8.7 kJ/mol (magnesium) | lowest | 7.95 kJ/mol (beryllium) | distribution | molar heat of vaporization | median | 139 kJ/mol | highest | 297 kJ/mol (beryllium) | lowest | 125 kJ/mol (radium) | distribution | specific heat at STP | median | 465 J/(kg K) | highest | 1820 J/(kg K) (beryllium) | lowest | 92 J/(kg K) (radium) | distribution | (properties at standard conditions)