Input interpretation
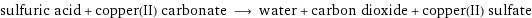
sulfuric acid + copper(II) carbonate ⟶ water + carbon dioxide + copper(II) sulfate
Balanced equation

Balance the chemical equation algebraically: + ⟶ + + Add stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, to the reactants and products: c_1 + c_2 ⟶ c_3 + c_4 + c_5 Set the number of atoms in the reactants equal to the number of atoms in the products for H, O, S, C and Cu: H: | 2 c_1 = 2 c_3 O: | 4 c_1 + 3 c_2 = c_3 + 2 c_4 + 4 c_5 S: | c_1 = c_5 C: | c_2 = c_4 Cu: | c_2 = c_5 Since the coefficients are relative quantities and underdetermined, choose a coefficient to set arbitrarily. To keep the coefficients small, the arbitrary value is ordinarily one. For instance, set c_1 = 1 and solve the system of equations for the remaining coefficients: c_1 = 1 c_2 = 1 c_3 = 1 c_4 = 1 c_5 = 1 Substitute the coefficients into the chemical reaction to obtain the balanced equation: Answer: | | + ⟶ + +
Structures
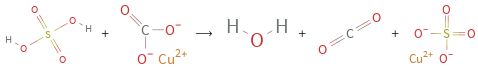
+ ⟶ + +
Names
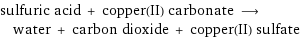
sulfuric acid + copper(II) carbonate ⟶ water + carbon dioxide + copper(II) sulfate
Reaction thermodynamics
Enthalpy
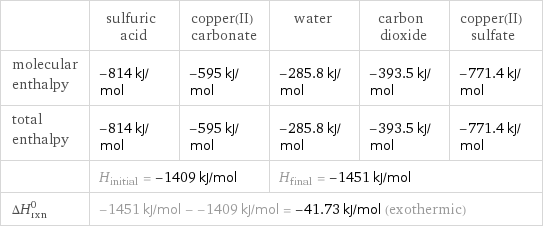
| sulfuric acid | copper(II) carbonate | water | carbon dioxide | copper(II) sulfate molecular enthalpy | -814 kJ/mol | -595 kJ/mol | -285.8 kJ/mol | -393.5 kJ/mol | -771.4 kJ/mol total enthalpy | -814 kJ/mol | -595 kJ/mol | -285.8 kJ/mol | -393.5 kJ/mol | -771.4 kJ/mol | H_initial = -1409 kJ/mol | | H_final = -1451 kJ/mol | | ΔH_rxn^0 | -1451 kJ/mol - -1409 kJ/mol = -41.73 kJ/mol (exothermic) | | | |
Gibbs free energy
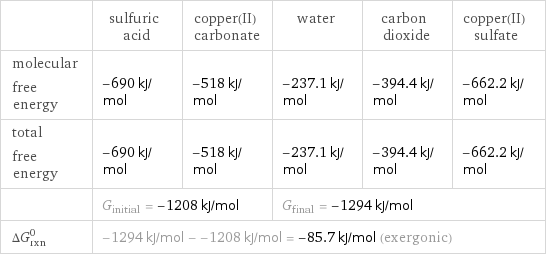
| sulfuric acid | copper(II) carbonate | water | carbon dioxide | copper(II) sulfate molecular free energy | -690 kJ/mol | -518 kJ/mol | -237.1 kJ/mol | -394.4 kJ/mol | -662.2 kJ/mol total free energy | -690 kJ/mol | -518 kJ/mol | -237.1 kJ/mol | -394.4 kJ/mol | -662.2 kJ/mol | G_initial = -1208 kJ/mol | | G_final = -1294 kJ/mol | | ΔG_rxn^0 | -1294 kJ/mol - -1208 kJ/mol = -85.7 kJ/mol (exergonic) | | | |
Equilibrium constant
![K_c = ([H2O] [CO2] [CuSO4])/([H2SO4] [CuCO3])](../image_source/b14e11c2ada836c9037f47a88361a4af.png)
K_c = ([H2O] [CO2] [CuSO4])/([H2SO4] [CuCO3])
Rate of reaction
![rate = -(Δ[H2SO4])/(Δt) = -(Δ[CuCO3])/(Δt) = (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) = (Δ[CO2])/(Δt) = (Δ[CuSO4])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)](../image_source/eba1ceffb274037d0a63749e717db451.png)
rate = -(Δ[H2SO4])/(Δt) = -(Δ[CuCO3])/(Δt) = (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) = (Δ[CO2])/(Δt) = (Δ[CuSO4])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)
Chemical names and formulas
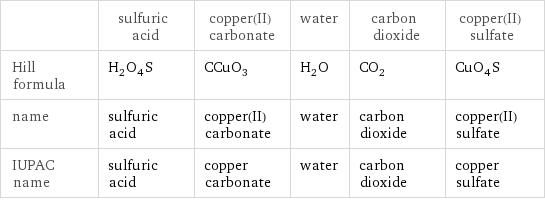
| sulfuric acid | copper(II) carbonate | water | carbon dioxide | copper(II) sulfate Hill formula | H_2O_4S | CCuO_3 | H_2O | CO_2 | CuO_4S name | sulfuric acid | copper(II) carbonate | water | carbon dioxide | copper(II) sulfate IUPAC name | sulfuric acid | copper carbonate | water | carbon dioxide | copper sulfate