Input interpretation

1-butanol | proton count
Result

Determine the number of protons in: 1-butanol (CH_3(CH_2)_3OH) Plan: • Use the summation: N_protons = sum_i N_i Z_i. • Determine the values of N_i and Z_i. • Compute the number of protons. Use the chemical formula, CH_3(CH_2)_3OH, to count the number of atoms, N_i, for each element: | N_i C | 4 H | 10 O | 1 Look up the atomic number, Z_i, for each element in the periodic table. The number of protons per atom is equal to the atomic number: | N_i | Z_i C | 4 | 6 H | 10 | 1 O | 1 | 8 Multiply N_i by Z_i to compute the number of protons for each element: | N_i | Z_i | N_i Z_i C | 4 | 6 | 4 × 6 = 24 H | 10 | 1 | 10 × 1 = 10 O | 1 | 8 | 1 × 8 = 8 Sum the N_i Z_i terms to compute the number of protons, N_protons: Answer: | | N_protons = 24 + 10 + 8 = 42
Particle counts
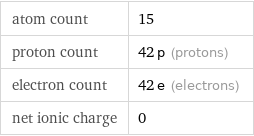
atom count | 15 proton count | 42 p (protons) electron count | 42 e (electrons) net ionic charge | 0
Corresponding quantity

Moles of protons from n = N/N_A: | 7×10^-23 mol (moles)