Input interpretation
oxygen gradient
Input values
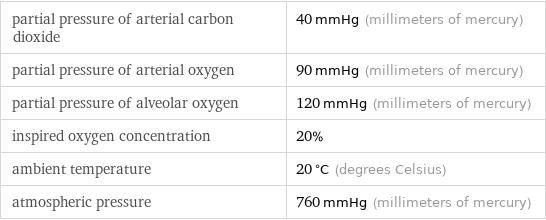
partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide | 40 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) partial pressure of arterial oxygen | 90 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) partial pressure of alveolar oxygen | 120 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) inspired oxygen concentration | 20% ambient temperature | 20 °C (degrees Celsius) atmospheric pressure | 760 mmHg (millimeters of mercury)
Result
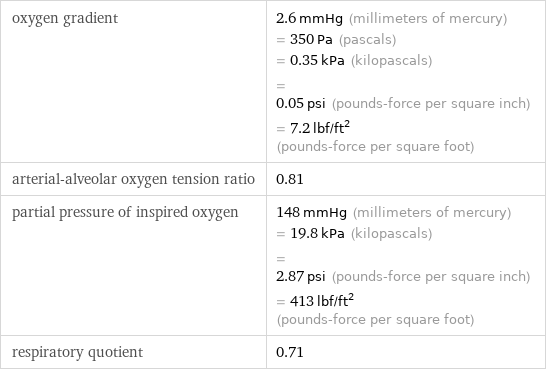
oxygen gradient | 2.6 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) = 350 Pa (pascals) = 0.35 kPa (kilopascals) = 0.05 psi (pounds-force per square inch) = 7.2 lbf/ft^2 (pounds-force per square foot) arterial-alveolar oxygen tension ratio | 0.81 partial pressure of inspired oxygen | 148 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) = 19.8 kPa (kilopascals) = 2.87 psi (pounds-force per square inch) = 413 lbf/ft^2 (pounds-force per square foot) respiratory quotient | 0.71