Input interpretation
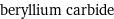
beryllium carbide
Chemical names and formulas

formula | CBe_2 name | beryllium carbide alternate names | beryllium acetylide | beryllium carbide (be2C) | beryllium dicarbide mass fractions | Be (beryllium) 60% | C (carbon) 40%
Lewis structure
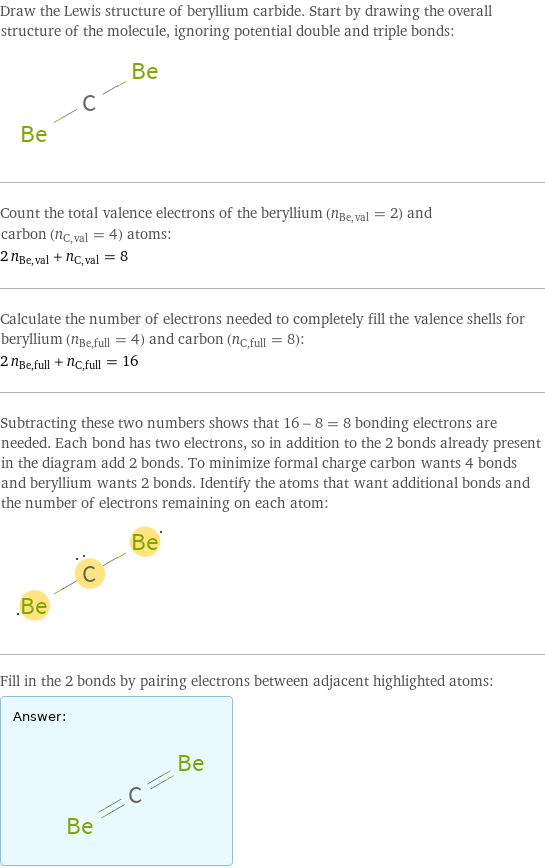
Draw the Lewis structure of beryllium carbide. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the beryllium (n_Be, val = 2) and carbon (n_C, val = 4) atoms: 2 n_Be, val + n_C, val = 8 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for beryllium (n_Be, full = 4) and carbon (n_C, full = 8): 2 n_Be, full + n_C, full = 16 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 16 - 8 = 8 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 2 bonds already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. To minimize formal charge carbon wants 4 bonds and beryllium wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
Basic properties
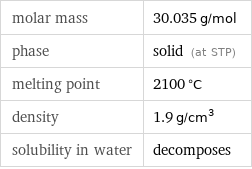
molar mass | 30.035 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 2100 °C density | 1.9 g/cm^3 solubility in water | decomposes
Units

Solid properties (at STP)

density | 1.9 g/cm^3
Units

Thermodynamic properties

molar heat of fusion | 75.3 kJ/mol specific heat of fusion | 2.51 kJ/g (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
![CAS number | 506-66-1 PubChem CID number | 68173 SMILES identifier | [Be]=C=[Be] InChI identifier | InChI=1/C.2Be/rCBe2/c2-1-3 EU number | 208-050-7 Gmelin number | 42330](../image_source/d09d2cdd33944f965e86963b5d08c997.png)
CAS number | 506-66-1 PubChem CID number | 68173 SMILES identifier | [Be]=C=[Be] InChI identifier | InChI=1/C.2Be/rCBe2/c2-1-3 EU number | 208-050-7 Gmelin number | 42330
NFPA label
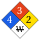
NFPA label
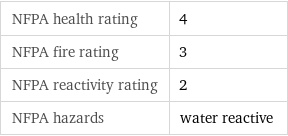
NFPA health rating | 4 NFPA fire rating | 3 NFPA reactivity rating | 2 NFPA hazards | water reactive
Toxicity properties

odor | odorless