Input interpretation

2-ethylhexyl methacrylate | orbital hybridization
Result
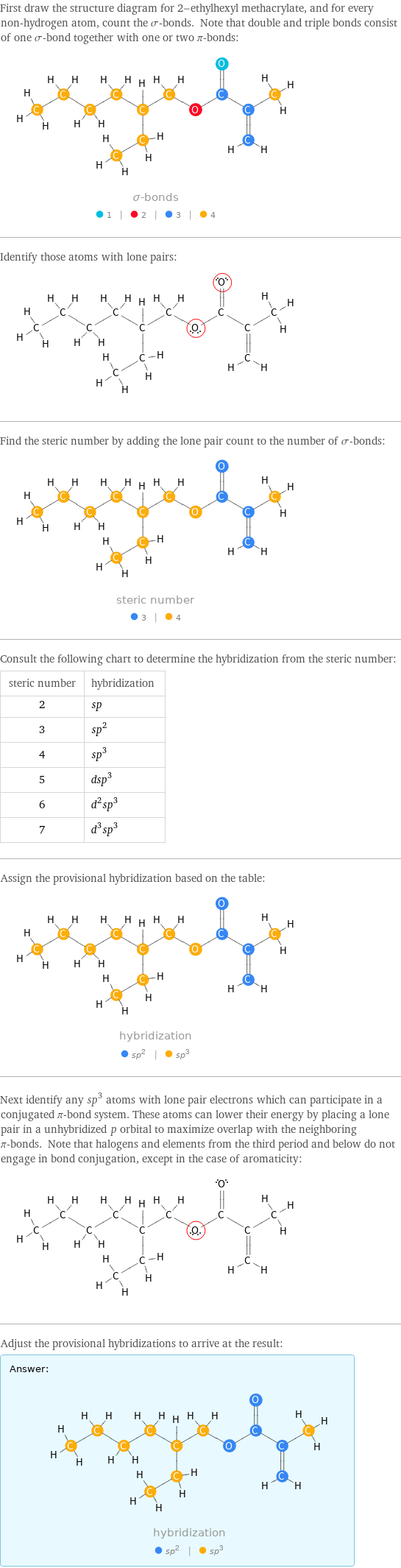
First draw the structure diagram for 2-ethylhexyl methacrylate, and for every non-hydrogen atom, count the σ-bonds. Note that double and triple bonds consist of one σ-bond together with one or two π-bonds: Identify those atoms with lone pairs: Find the steric number by adding the lone pair count to the number of σ-bonds: Consult the following chart to determine the hybridization from the steric number: steric number | hybridization 2 | sp 3 | sp^2 4 | sp^3 5 | dsp^3 6 | d^2sp^3 7 | d^3sp^3 Assign the provisional hybridization based on the table: Next identify any sp^3 atoms with lone pair electrons which can participate in a conjugated π-bond system. These atoms can lower their energy by placing a lone pair in a unhybridized p orbital to maximize overlap with the neighboring π-bonds. Note that halogens and elements from the third period and below do not engage in bond conjugation, except in the case of aromaticity: Adjust the provisional hybridizations to arrive at the result: Answer: | |
Chemical names and formulas
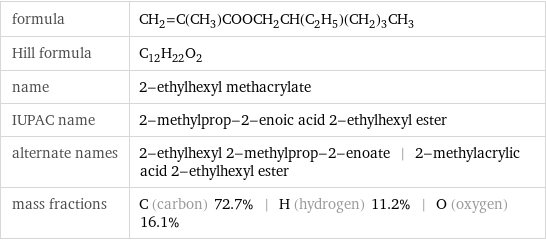
formula | CH_2=C(CH_3)COOCH_2CH(C_2H_5)(CH_2)_3CH_3 Hill formula | C_12H_22O_2 name | 2-ethylhexyl methacrylate IUPAC name | 2-methylprop-2-enoic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester alternate names | 2-ethylhexyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate | 2-methylacrylic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester mass fractions | C (carbon) 72.7% | H (hydrogen) 11.2% | O (oxygen) 16.1%