Input interpretation

weak bases | melting point
Summary

median | -67.6 °C highest | 1 °C (diazane) lowest | -117 °C (trimethylamine) distribution | | (based on 10 values; 3 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
hydroxylamine | aluminum hydroxide | iron(II) hydroxide (total: 3)
Distribution plots
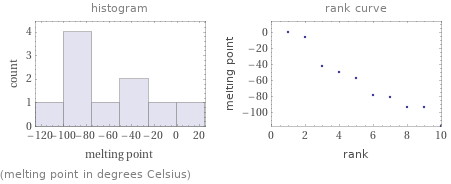
(melting point in degrees Celsius)
Melting point rankings
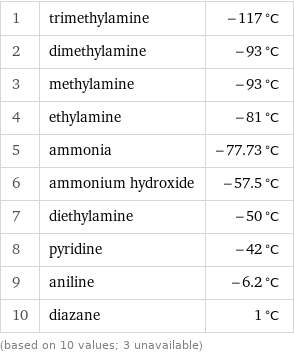
1 | trimethylamine | -117 °C 2 | dimethylamine | -93 °C 3 | methylamine | -93 °C 4 | ethylamine | -81 °C 5 | ammonia | -77.73 °C 6 | ammonium hydroxide | -57.5 °C 7 | diethylamine | -50 °C 8 | pyridine | -42 °C 9 | aniline | -6.2 °C 10 | diazane | 1 °C (based on 10 values; 3 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median melting point -67.6 °C
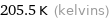
205.5 K (kelvins)

-89.7 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

370 °R (degrees Rankine)
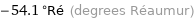
-54.1 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
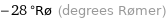
-28 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median melting point -67.6 °C
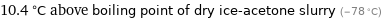
10.4 °C above boiling point of dry ice-acetone slurry (-78 °C)
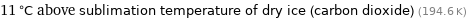
11 °C above sublimation temperature of dry ice (carbon dioxide) (194.6 K)

27 °C above coldest recorded temperature on Earth (-94.7 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 18 meV (millielectronvolts)
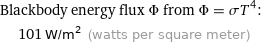
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 101 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 2.9×10^-34 lx (lux)