Input interpretation
acetaminophen
Chemical names and formulas

formula | CH_3CONHC_6H_4OH Hill formula | C_8H_9NO_2 name | acetaminophen IUPAC name | N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide alternate names | 4-acetamidophenol | 4'-hydroxyacetanilide | abensanil | acetagesic | anelix | datril | lonarid | multin | N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide | N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanamide | N-acetyl-4-aminophenol | N-acetyl-para-aminophenol | naprinol | tylenol mass fractions | C (carbon) 63.6% | H (hydrogen) 6% | N (nitrogen) 9.27% | O (oxygen) 21.2%
Lewis structure
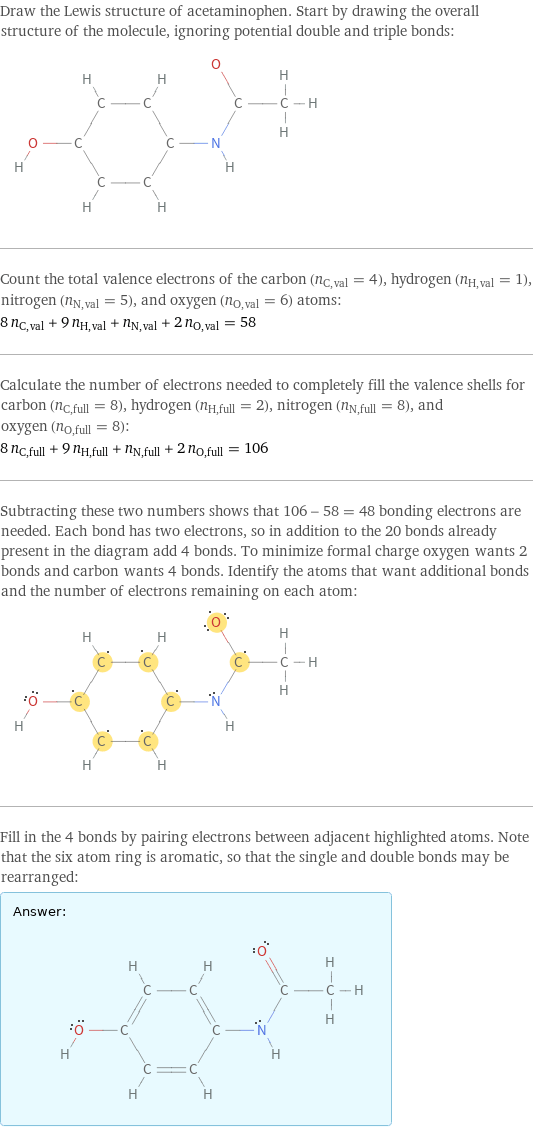
Draw the Lewis structure of acetaminophen. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 8 n_C, val + 9 n_H, val + n_N, val + 2 n_O, val = 58 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 8 n_C, full + 9 n_H, full + n_N, full + 2 n_O, full = 106 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 106 - 58 = 48 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 20 bonds already present in the diagram add 4 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 4 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom ring is aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
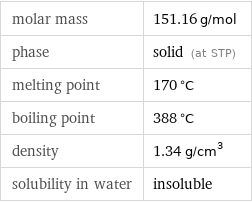
molar mass | 151.16 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 170 °C boiling point | 388 °C density | 1.34 g/cm^3 solubility in water | insoluble
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 0.4 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 0.51 experimental LogS | -1.03 predicted LogS | -1.56
Drug interactions
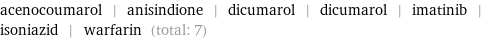
acenocoumarol | anisindione | dicumarol | dicumarol | imatinib | isoniazid | warfarin (total: 7)
Basic drug properties
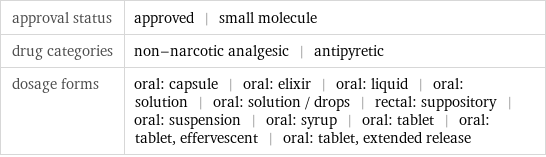
approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | non-narcotic analgesic | antipyretic dosage forms | oral: capsule | oral: elixir | oral: liquid | oral: solution | oral: solution / drops | rectal: suppository | oral: suspension | oral: syrup | oral: tablet | oral: tablet, effervescent | oral: tablet, extended release

brand names | abenol | abensanil | acamol | accu-tap | acephen | aceta elixir | aceta tablets | acetagesic | acetalgin | actamin | actimol | algotropyl | allay | alpiny | alpinyl | alvedon | amadil | aminofen | anacin | anacin-3 | anaflon | anapap | anelix | anhiba | apacet | apadon | apamid | apamide | atasol | banesin | bayer select | bickie-mol | bucet | butapap | calpol | captin | cetadol | clixodyne | Co-gesic | conacetol | dafalgan | dapa | dapa X-S | darvocet | datril | dimindol | dirox | disprol | dolene AP-65 | doliprane | dolprone | drixoral plus | dularin | dymadon | dypap | elixodyne | enelfa | eneril | Eu-med | excedrin | exdol | febridol | febrilix | febrinol | febro-gesic | febrolin | fendon | feverall | fevor | finimal | gelocatil | genapap | genebs | hedex | homoolan | Hy-phen | injectapap | janupap | korum | lestemp | liquagesic | liquiprin | lonarid | lyteca | momentum | multin | NAPA | napafen | napap | naprinol | nealgyl | nebs | neopap | neotrend | nobedon | norco | oraphen-PD | ortensan | pacemo | painex | paldesic | panadol | panaleve | panasorb | panets | panex | panofen | papa-deine | paracet | parapan | paraspen | parelan | parmol | pasolind | pasolind N | pedric | phenaphen | phenaphen caplets | phendon | phrenilin | phrenilin forte | prompt | propacet 100 | proval #3 | pyrinazine | redutemp | rivalgyl | robigesic | rounox | SK-apap | salzone | sedapap | servigesic | snaplets-FR | St. joseph fever reducer | suppap | synalgos-Dc-A | tabalgin | talacen | tapanol | tapar | tavist allergy/sinus/headache | temlo | tempanal | tempra | tencon | tibinide | tibizide | tisin | tisiodrazida | tizide | tralgon | triaprin | tussapap | tycolet | tylenol | ultracet | valadol | valgesic | valorin | valorin extra | wygesic
Solid properties (at STP)

density | 1.34 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 1×10^-6 mmHg (at 25 °C)
Units

Thermodynamic properties
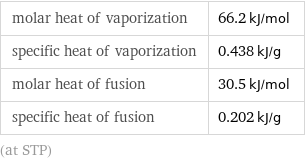
molar heat of vaporization | 66.2 kJ/mol specific heat of vaporization | 0.438 kJ/g molar heat of fusion | 30.5 kJ/mol specific heat of fusion | 0.202 kJ/g (at STP)
Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 103-90-2 Beilstein number | 2208089 PubChem CID number | 1983 PubChem SID number | 24891200 SMILES identifier | CC(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)O InChI identifier | InChI=1/C8H9NO2/c1-6(10)9-7-2-4-8(11)5-3-7/h2-5, 11H, 1H3, (H, 9, 10)/f/h9H InChI key | RZVAJINKPMORJF-BGGKNDAXCW RTECS number | AE4200000 MDL number | MFCD00002328
Safety properties

flash point | 188 °C autoignition point | 540 °C
Toxicity properties

odor | odorless

RTECS classes | tumorigen | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data