Input interpretation

refrigerants | melting point
Summary
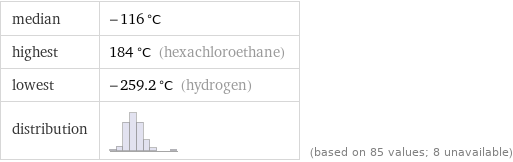
median | -116 °C highest | 184 °C (hexachloroethane) lowest | -259.2 °C (hydrogen) distribution | | (based on 85 values; 8 unavailable)
Entities with missing values

helium | chloroethane | norflurane | 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl methyl ether | 1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3-hexafluoropropane | 1, 1, 1, 2-tetrachloro-2, 2-difluoroethane | 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrachloro-1, 2-difluoroethane | hexafluoropropene, trimer (total: 8)
Distribution plots
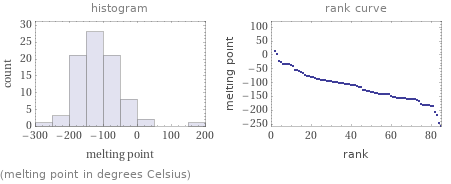
(melting point in degrees Celsius)
Melting point rankings
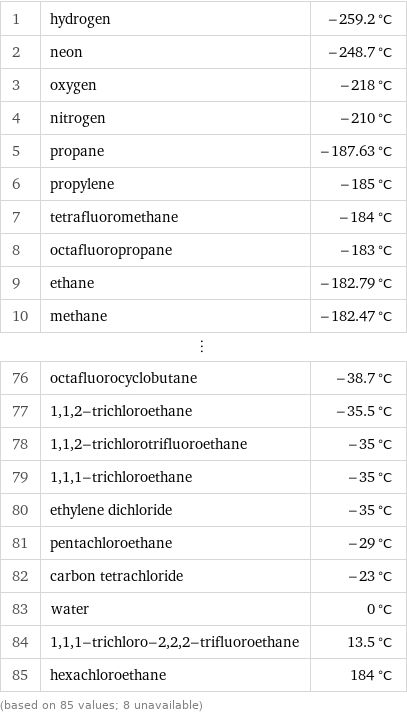
1 | hydrogen | -259.2 °C 2 | neon | -248.7 °C 3 | oxygen | -218 °C 4 | nitrogen | -210 °C 5 | propane | -187.63 °C 6 | propylene | -185 °C 7 | tetrafluoromethane | -184 °C 8 | octafluoropropane | -183 °C 9 | ethane | -182.79 °C 10 | methane | -182.47 °C ⋮ | | 76 | octafluorocyclobutane | -38.7 °C 77 | 1, 1, 2-trichloroethane | -35.5 °C 78 | 1, 1, 2-trichlorotrifluoroethane | -35 °C 79 | 1, 1, 1-trichloroethane | -35 °C 80 | ethylene dichloride | -35 °C 81 | pentachloroethane | -29 °C 82 | carbon tetrachloride | -23 °C 83 | water | 0 °C 84 | 1, 1, 1-trichloro-2, 2, 2-trifluoroethane | 13.5 °C 85 | hexachloroethane | 184 °C (based on 85 values; 8 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median melting point -116 °C
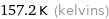
157.2 K (kelvins)

-176.8 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
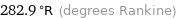
282.9 °R (degrees Rankine)
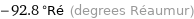
-92.8 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

-53.4 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median melting point -116 °C
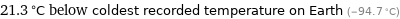
21.3 °C below coldest recorded temperature on Earth (-94.7 °C)
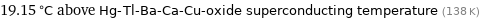
19.15 °C above Hg-Tl-Ba-Ca-Cu-oxide superconducting temperature (138 K)
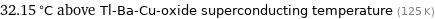
32.15 °C above Tl-Ba-Cu-oxide superconducting temperature (125 K)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 14 meV (millielectronvolts)
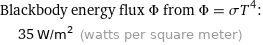
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 35 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 1.5×10^-46 lx (lux)