Input interpretation

water | phase | gas
Thermodynamic properties of matter
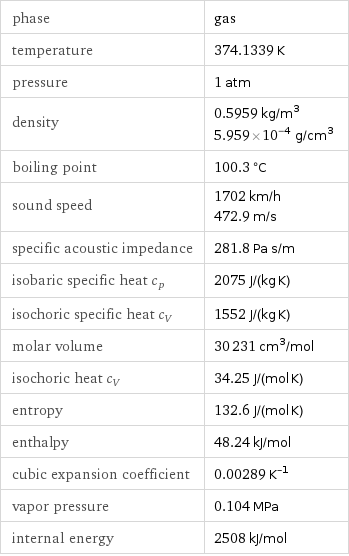
phase | gas temperature | 374.1339 K pressure | 1 atm density | 0.5959 kg/m^3 5.959×10^-4 g/cm^3 boiling point | 100.3 °C sound speed | 1702 km/h 472.9 m/s specific acoustic impedance | 281.8 Pa s/m isobaric specific heat c_p | 2075 J/(kg K) isochoric specific heat c_V | 1552 J/(kg K) molar volume | 30231 cm^3/mol isochoric heat c_V | 34.25 J/(mol K) entropy | 132.6 J/(mol K) enthalpy | 48.24 kJ/mol cubic expansion coefficient | 0.00289 K^(-1) vapor pressure | 0.104 MPa internal energy | 2508 kJ/mol
Phase diagram
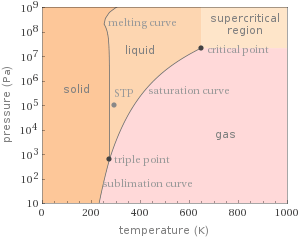
Phase diagram
Units
Lewis structure
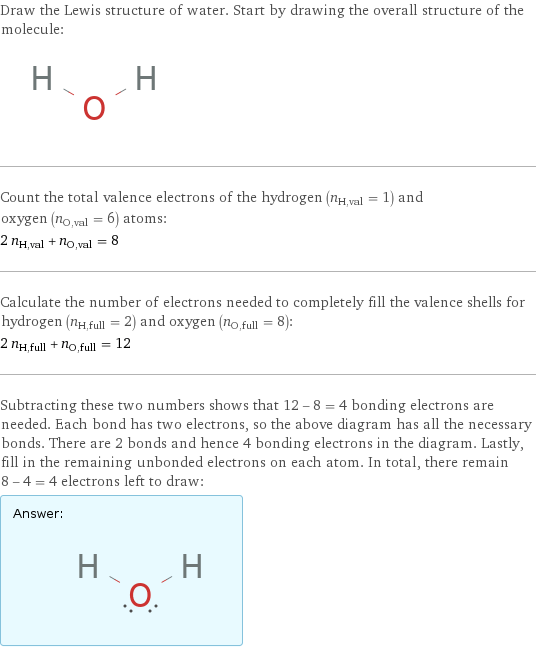
Draw the Lewis structure of water. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 2 n_H, val + n_O, val = 8 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for hydrogen (n_H, full = 2) and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 2 n_H, full + n_O, full = 12 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 12 - 8 = 4 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 2 bonds and hence 4 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 8 - 4 = 4 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
3D structure

3D structure
Basic properties
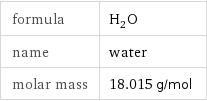
formula | H_2O name | water molar mass | 18.015 g/mol
Units

Chemical identifiers
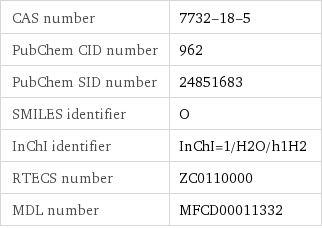
CAS number | 7732-18-5 PubChem CID number | 962 PubChem SID number | 24851683 SMILES identifier | O InChI identifier | InChI=1/H2O/h1H2 RTECS number | ZC0110000 MDL number | MFCD00011332