Input interpretation

liquid elements (at STP) | critical temperature
Results
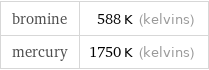
bromine | 588 K (kelvins) mercury | 1750 K (kelvins)

liquid elements (at STP) | critical temperature | 1169 K (kelvins) (median)
Relative values
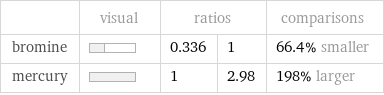
| visual | ratios | | comparisons bromine | | 0.336 | 1 | 66.4% smaller mercury | | 1 | 2.98 | 198% larger
Unit conversions for median critical temperature 1169 K

896 °C (degrees Celsius)

1645 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
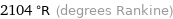
2104 °R (degrees Rankine)

717 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
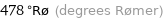
478 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median critical temperature 1169 K
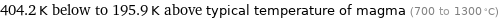
404.2 K below to 195.9 K above typical temperature of magma (700 to 1300 °C)
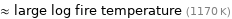
≈ large log fire temperature (1170 K)
Corresponding quantities
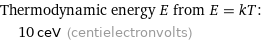
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 10 ceV (centielectronvolts)
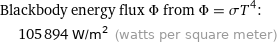
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 105894 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)
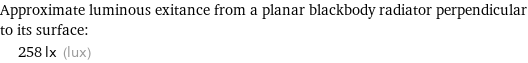
Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 258 lx (lux)