Input interpretation
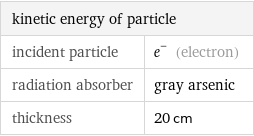
kinetic energy of particle | incident particle | e^- (electron) radiation absorber | gray arsenic thickness | 20 cm
Result

26 GeV (gigaelectronvolts)
Comparison as energy for 26 GeV
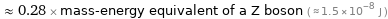
≈ 0.28 × mass-energy equivalent of a Z boson ( ≈ 1.5×10^-8 J )
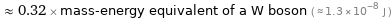
≈ 0.32 × mass-energy equivalent of a W boson ( ≈ 1.3×10^-8 J )

≈ 0.52 × initial per beam operating energy of the CERN Large Electron Positron Collider in 1983 ( ≈ 8×10^-9 J )
Comparison as kinetic energy for 26 GeV
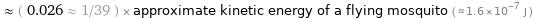
≈ ( 0.026 ≈ 1/39 ) × approximate kinetic energy of a flying mosquito ( ≈ 1.6×10^-7 J )
Absorber material properties
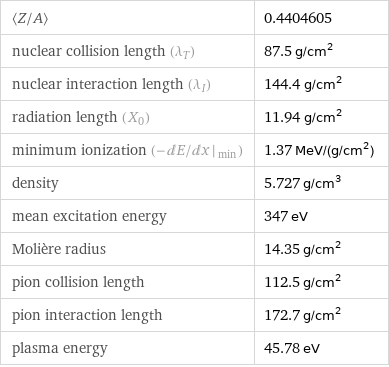
〈Z/A〉 | 0.4404605 nuclear collision length (λ_T) | 87.5 g/cm^2 nuclear interaction length (λ_I) | 144.4 g/cm^2 radiation length (X_0) | 11.94 g/cm^2 minimum ionization (- dE/ dx |_ min) | 1.37 MeV/(g/cm^2) density | 5.727 g/cm^3 mean excitation energy | 347 eV Molière radius | 14.35 g/cm^2 pion collision length | 112.5 g/cm^2 pion interaction length | 172.7 g/cm^2 plasma energy | 45.78 eV