Input interpretation
sulfamic acid
Chemical names and formulas

formula | NH_2SO_3H Hill formula | H_3NO_3S name | sulfamic acid alternate names | amidosulfonic acid | amidosulfuric acid | jumbo | sulfamidic acid | sulfaminic acid | sulphamic acid mass fractions | H (hydrogen) 3.11% | N (nitrogen) 14.4% | O (oxygen) 49.4% | S (sulfur) 33%
Lewis structure
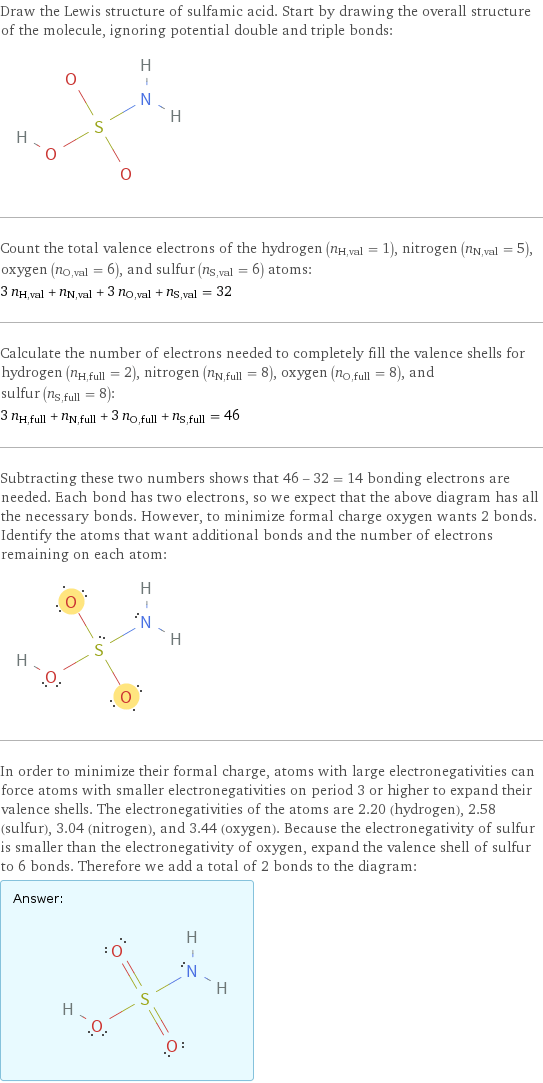
Draw the Lewis structure of sulfamic acid. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), oxygen (n_O, val = 6), and sulfur (n_S, val = 6) atoms: 3 n_H, val + n_N, val + 3 n_O, val + n_S, val = 32 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), oxygen (n_O, full = 8), and sulfur (n_S, full = 8): 3 n_H, full + n_N, full + 3 n_O, full + n_S, full = 46 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 46 - 32 = 14 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so we expect that the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. However, to minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: In order to minimize their formal charge, atoms with large electronegativities can force atoms with smaller electronegativities on period 3 or higher to expand their valence shells. The electronegativities of the atoms are 2.20 (hydrogen), 2.58 (sulfur), 3.04 (nitrogen), and 3.44 (oxygen). Because the electronegativity of sulfur is smaller than the electronegativity of oxygen, expand the valence shell of sulfur to 6 bonds. Therefore we add a total of 2 bonds to the diagram: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
molar mass | 97.09 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 220 °C boiling point | 247 °C density | 2.15 g/cm^3
Units

Solid properties (at STP)
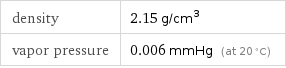
density | 2.15 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 0.006 mmHg (at 20 °C)
Units

Thermodynamic properties

molar heat of combustion | 1530 kJ/mol specific heat of combustion | 15.76 kJ/g molar heat of fusion | 11.9 kJ/mol specific heat of fusion | 0.1226 kJ/g (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
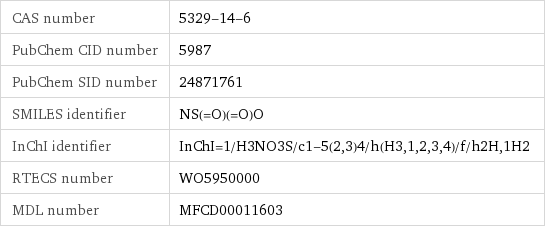
CAS number | 5329-14-6 PubChem CID number | 5987 PubChem SID number | 24871761 SMILES identifier | NS(=O)(=O)O InChI identifier | InChI=1/H3NO3S/c1-5(2, 3)4/h(H3, 1, 2, 3, 4)/f/h2H, 1H2 RTECS number | WO5950000 MDL number | MFCD00011603
NFPA label

NFPA label
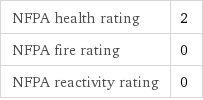
NFPA health rating | 2 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties

flash point | 205 °C
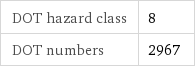
DOT hazard class | 8 DOT numbers | 2967
Toxicity properties
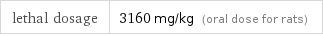
lethal dosage | 3160 mg/kg (oral dose for rats)

probable lethal dose for man | 600 mL (milliliters) RTECS classes | agricultural chemical and pesticide | primary irritant