Input interpretation

water
Chemical names and formulas

formula | H_2O name | water alternate names | dihydrogen monoxide | distilled water | hydrogen hydroxide | oxidane mass fractions | H (hydrogen) 11.2% | O (oxygen) 88.8%
Lewis structure
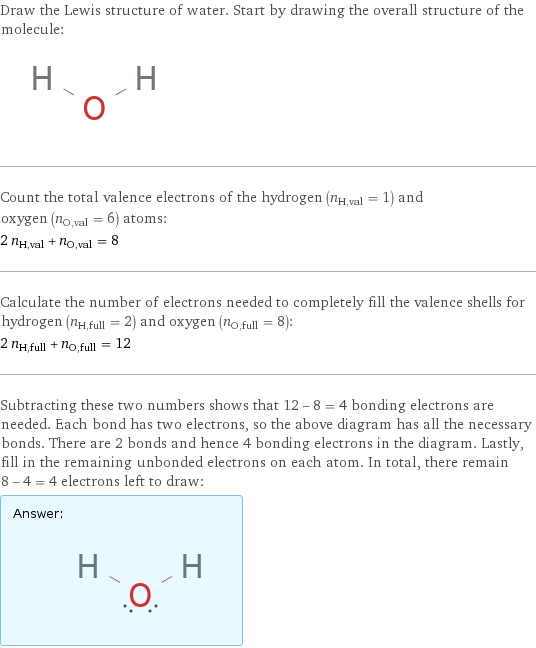
Draw the Lewis structure of water. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 2 n_H, val + n_O, val = 8 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for hydrogen (n_H, full = 2) and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 2 n_H, full + n_O, full = 12 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 12 - 8 = 4 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 2 bonds and hence 4 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 8 - 4 = 4 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
3D structure

3D structure
Basic properties
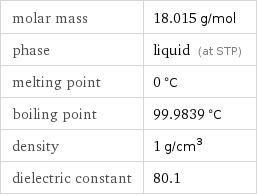
molar mass | 18.015 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | 0 °C boiling point | 99.9839 °C density | 1 g/cm^3 dielectric constant | 80.1
Liquid properties (at STP)
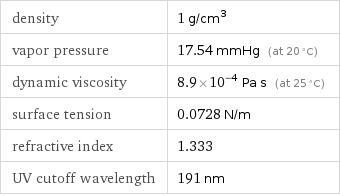
density | 1 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 17.54 mmHg (at 20 °C) dynamic viscosity | 8.9×10^-4 Pa s (at 25 °C) surface tension | 0.0728 N/m refractive index | 1.333 UV cutoff wavelength | 191 nm
Units

Thermodynamic properties
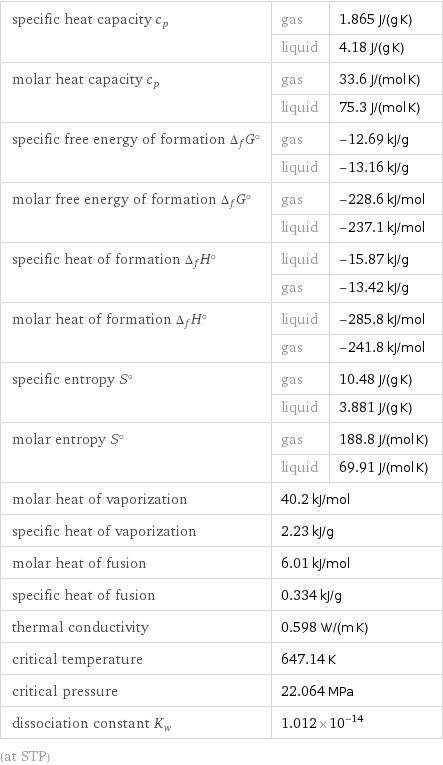
specific heat capacity c_p | gas | 1.865 J/(g K) | liquid | 4.18 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | gas | 33.6 J/(mol K) | liquid | 75.3 J/(mol K) specific free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | -12.69 kJ/g | liquid | -13.16 kJ/g molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | -228.6 kJ/mol | liquid | -237.1 kJ/mol specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | liquid | -15.87 kJ/g | gas | -13.42 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | liquid | -285.8 kJ/mol | gas | -241.8 kJ/mol specific entropy S° | gas | 10.48 J/(g K) | liquid | 3.881 J/(g K) molar entropy S° | gas | 188.8 J/(mol K) | liquid | 69.91 J/(mol K) molar heat of vaporization | 40.2 kJ/mol | specific heat of vaporization | 2.23 kJ/g | molar heat of fusion | 6.01 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.334 kJ/g | thermal conductivity | 0.598 W/(m K) | critical temperature | 647.14 K | critical pressure | 22.064 MPa | dissociation constant K_w | 1.012×10^-14 | (at STP)
Phase diagram
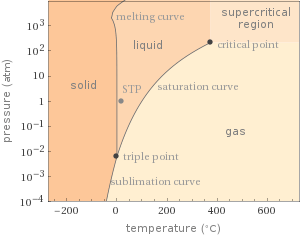
Phase diagram
Units
