Input interpretation
2 kg of nonane
Basic properties for 2 kg
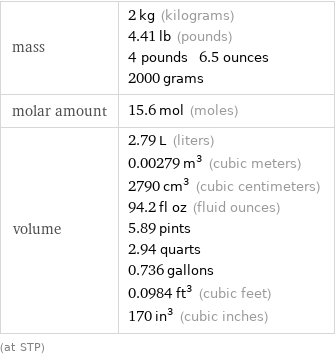
mass | 2 kg (kilograms) 4.41 lb (pounds) 4 pounds 6.5 ounces 2000 grams molar amount | 15.6 mol (moles) volume | 2.79 L (liters) 0.00279 m^3 (cubic meters) 2790 cm^3 (cubic centimeters) 94.2 fl oz (fluid ounces) 5.89 pints 2.94 quarts 0.736 gallons 0.0984 ft^3 (cubic feet) 170 in^3 (cubic inches) (at STP)
Corresponding quantities
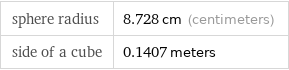
sphere radius | 8.728 cm (centimeters) side of a cube | 0.1407 meters
Thermodynamic properties for 2 kg
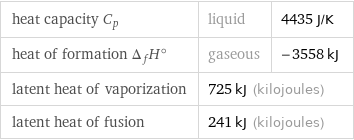
heat capacity C_p | liquid | 4435 J/K heat of formation Δ_fH° | gaseous | -3558 kJ latent heat of vaporization | 725 kJ (kilojoules) | latent heat of fusion | 241 kJ (kilojoules) |
Units
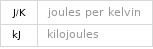
Energy vs. temperature for 2 kg
(relative to STP)
Units

Phase change energies for 2 kg from 25 °C

energy required to heat to boiling point | 559 kJ (kilojoules) energy required to convert to vapor | 725 kJ (kilojoules) energy required to heat to boiling point and convert to vapor | 1280 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from cooling to freezing point | 346 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from converting to solid | 241 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from cooling to freezing point and converting to solid | 587 kJ (kilojoules)
Mass composition for 2 kg
C (carbon) | 1.686 kg (84.3%) H (hydrogen) | 0.314 kg (15.7%)
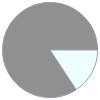
Mass composition for 2 kg
Lewis structure
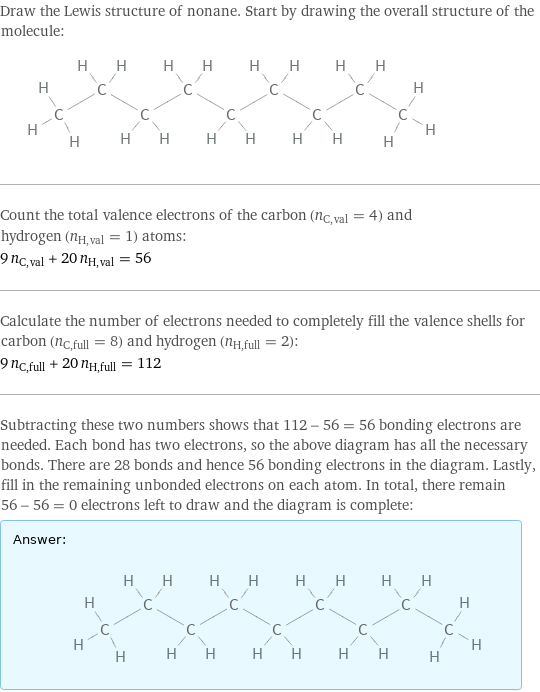
Draw the Lewis structure of nonane. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4) and hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) atoms: 9 n_C, val + 20 n_H, val = 56 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8) and hydrogen (n_H, full = 2): 9 n_C, full + 20 n_H, full = 112 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 112 - 56 = 56 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 28 bonds and hence 56 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 56 - 56 = 0 electrons left to draw and the diagram is complete: Answer: | |
Chemical names and formulas
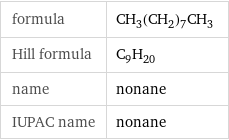
formula | CH_3(CH_2)_7CH_3 Hill formula | C_9H_20 name | nonane IUPAC name | nonane