Input interpretation

gaseous elements (at STP) | atomic diameter
Summary
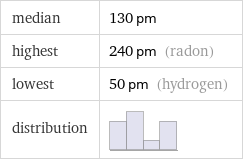
median | 130 pm highest | 240 pm (radon) lowest | 50 pm (hydrogen) distribution |
Units

Plot
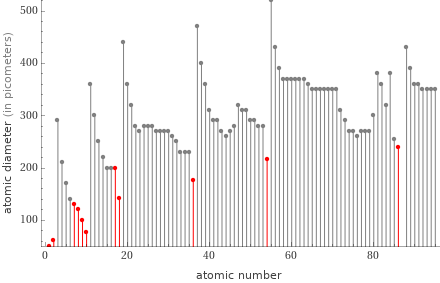
Plot
Periodic table location
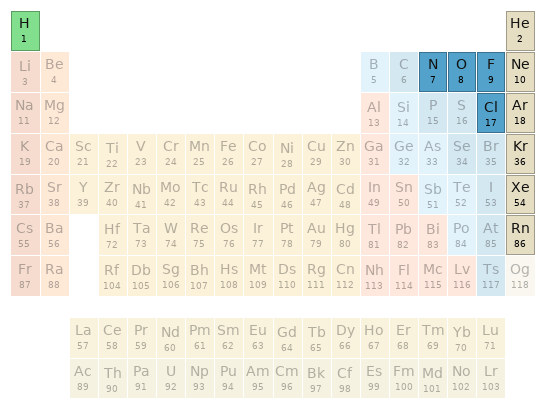
Periodic table location
Atomic radii properties
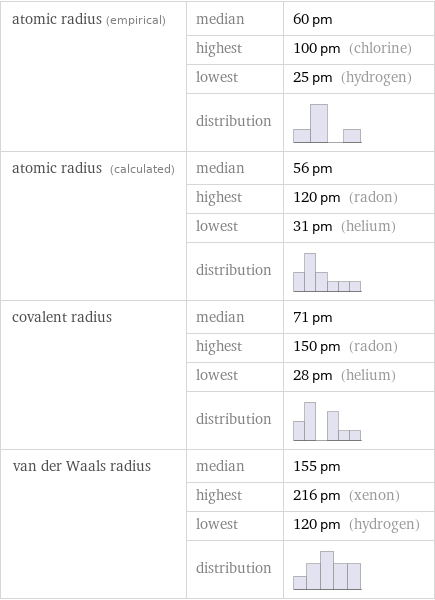
atomic radius (empirical) | median | 60 pm | highest | 100 pm (chlorine) | lowest | 25 pm (hydrogen) | distribution | atomic radius (calculated) | median | 56 pm | highest | 120 pm (radon) | lowest | 31 pm (helium) | distribution | covalent radius | median | 71 pm | highest | 150 pm (radon) | lowest | 28 pm (helium) | distribution | van der Waals radius | median | 155 pm | highest | 216 pm (xenon) | lowest | 120 pm (hydrogen) | distribution |
Units

Distribution plots
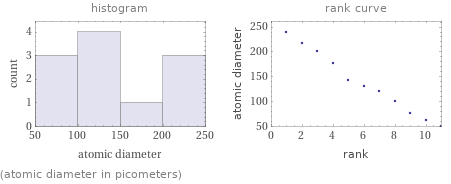
(atomic diameter in picometers)
Atomic diameter rankings
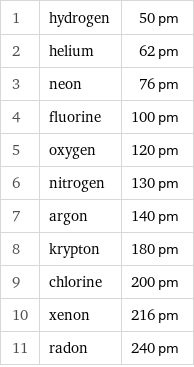
1 | hydrogen | 50 pm 2 | helium | 62 pm 3 | neon | 76 pm 4 | fluorine | 100 pm 5 | oxygen | 120 pm 6 | nitrogen | 130 pm 7 | argon | 140 pm 8 | krypton | 180 pm 9 | chlorine | 200 pm 10 | xenon | 216 pm 11 | radon | 240 pm
Unit conversions for median atomic diameter 130 pm
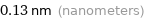
0.13 nm (nanometers)
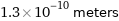
1.3×10^-10 meters
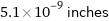
5.1×10^-9 inches
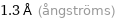
1.3 Å (ångströms)
Comparisons for median atomic diameter 130 pm
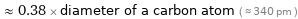
≈ 0.38 × diameter of a carbon atom ( ≈ 340 pm )
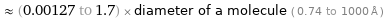
≈ (0.00127 to 1.7) × diameter of a molecule ( 0.74 to 1000 Å )
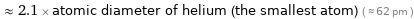
≈ 2.1 × atomic diameter of helium (the smallest atom) ( ≈ 62 pm )